What Everyone Should Know About Bed Bugs and Their Habitat
Bed Bug Habitats and Behavior
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are notorious pests that thrive primarily in close proximity to humans, as they rely on our blood for sustenance. Their preferred habitats include bedrooms and areas where people sleep, as well as furniture, clothing, and luggage. They exhibit a distinct preference for dark, warm, and secluded spaces, which makes it challenging to detect their presence until a significant infestation occurs.
When searching for potential hiding spots, it is vital to inspect various household items. Common locations include the seams and folds of mattresses and box springs, behind headboards, and within bed frames. Bed bugs can also occupy crevices in furniture, such as chairs and couches, making them difficult to eliminate. Additionally, infested clothing, suitcases, and other belongings can serve as transportation vectors, spreading these pests to new locations.
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal creatures, displaying increased activity during the night when they emerge to feed on their hosts. Their feeding sessions typically last between five to ten minutes. It is important to note that bed bugs do not feed daily; rather, they can survive for several months without a meal, depending on environmental conditions. Temperature plays a significant role in bed bug behavior; they tend to be more active in warmer conditions, and extreme cold can be detrimental to their survival.
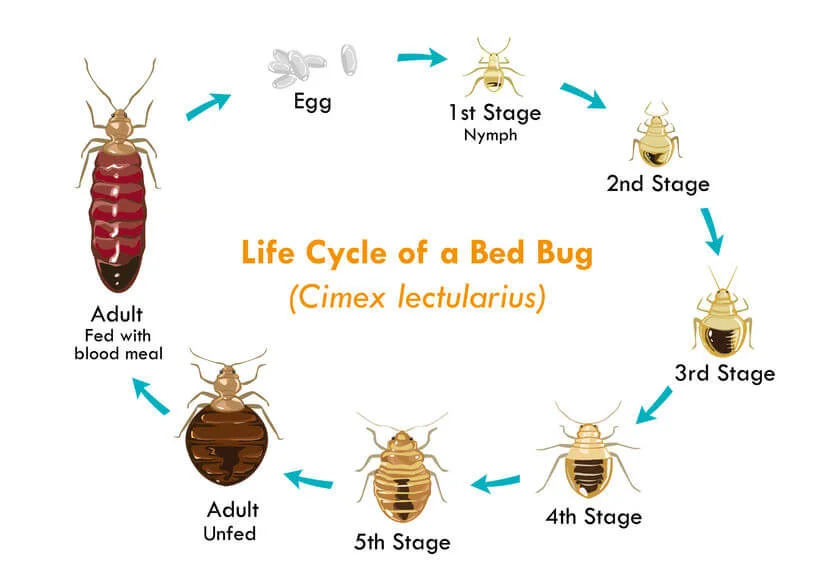
Understanding Bed Bugs: An Overview
Bed bugs, scientifically classified as Cimex lectularius, are small, wingless insects that belong to the family Cimicidae. Adult bed bugs typically measure between 4 to 5 millimeters in length and have a flat, oval body that enables them to hide in narrow crevices. Their coloration ranges from reddish-brown to tan, depending on their feeding status; a blood-fed bed bug appears darker and more swollen. Bed bugs are most active during the night, and they feed on human blood by piercing the skin with specialized mouthparts, often leaving itchy welts in their wake.
The life cycle of a bed bug progresses from egg to nymph to adult, with females laying up to five eggs per day. These eggs hatch within one to two weeks under favorable conditions, contributing to rapid population growth. A nymph undergoes several molts before reaching adulthood, during which it requires a blood meal at each stage. This adaptability and reproductive capacity are significant factors that make bed bugs a concern for households worldwide.
While bed bugs do not transmit diseases, their presence can lead to considerable discomfort and stress. Bites can cause varying reactions, from mild irritation to severe allergic responses, necessitating medical attention in some instances. The psychological impact of bed bug infestations is equally concerning, with individuals experiencing anxiety and disturbed sleep due to fear of bites or the stigma associated with these pests.
Historically, bed bugs have plagued humanity for centuries, with evidence of their presence dating back to ancient civilizations. Their population saw a decline in the mid-20th century due to the widespread use of pesticides, but they have since made a resurgence, particularly in urban areas. This resurgence is attributed to factors including increased international travel, resistance to pesticides, and a lack of public awareness regarding their prevention and control.
Identifying Bed Bug Infestations
Detecting a bed bug infestation in a timely manner is crucial for effective management and eradication. Adult bed bugs are small, typically about the size of an apple seed, and have a flat, oval shape that can make them hard to spot. They are usually a rusty brown color, though they may appear lighter or darker depending on their stage of feeding. When inspecting for bed bugs, it is essential to check common hiding places in and around the bed, including seams of mattresses, box springs, headboards, and even nightstands.
Nymphs, which are the immature stages of bed bugs, resemble adults but are smaller and lighter in color. At times, bed bug eggs are present as well; these are tiny, white, and somewhat difficult to see without close inspection. Checking for eggs often involves looking in crevices and along the edges of furniture. Various signs indicate a bed bug presence, including shed skins, fecal spots, or the occasional blood stain on bedding, which can occur when an individual inadvertently crushes a feeding bug.
Another common indicator of a bed bug infestation is the appearance of bites on the skin. Typically, these bites result in small, red, itchy welts, often organized in a line or cluster, usually manifesting on areas such as the arms, neck, or legs. It’s important to note that some individuals may not react to bed bug bites at all, which can lead to a delayed identification of the problem.
Regular inspections of sleeping areas and associated furniture will provide early warning signs of a potential infestation. By conducting thorough examinations, one can catch bed bugs before a full-fledged invasion occurs. Implementing preventative measures, such as encasements for mattresses and schedules for routine checks, can greatly reduce the risk of experiencing a bed bug issue.
Preventing and Managing Bed Bug Infestations
Effective prevention and management of bed bug infestations require a multifaceted approach. One key strategy is to maintain a high standard of cleanliness in living spaces. Regular vacuuming of carpets, rugs, and upholstered furniture helps eliminate any potential bed bugs or their eggs. It is essential to use a vacuum with a HEPA filter and to dispose of the vacuum bag immediately to prevent reinfestation. Additionally, bed linens and clothing should be washed in hot water regularly, as extreme temperatures can kill bed bugs.
Encasing mattresses and box springs with bed bug-proof covers is another effective measure. These specially designed encasements prevent bed bugs from entering or escaping, effectively cutting off their habitat. When selecting mattress encasements, ensure they are durable and have sealed zippers to offer maximum protection against infestations.
Regular inspections are also crucial for early detection of bed bugs. Thoroughly checking sleeping areas, particularly the seams and folds of mattresses, behind bed frames, and around baseboards can help spot any signs of bed bugs before they proliferate. It is advisable to conduct these inspections periodically, especially after staying in hotels or using public transportation where bed bugs may be present.
For those who encounter an infestation, various treatment options are available. Home remedies, such as diatomaceous earth or essential oils, can provide preliminary relief. However, for severe infestations, professional pest control services are often necessary. Exterminators have access to specialized insecticides and methods that ensure thorough eradication of bed bugs while minimizing risks to inhabitants. Special care must be taken in public places like hotels or public transport. Educating staff about bed bug prevention and implementing routine inspections can significantly reduce the chances of infestations spreading in these environments.
What Our Customers Say




